What is the purpose of an inverter?
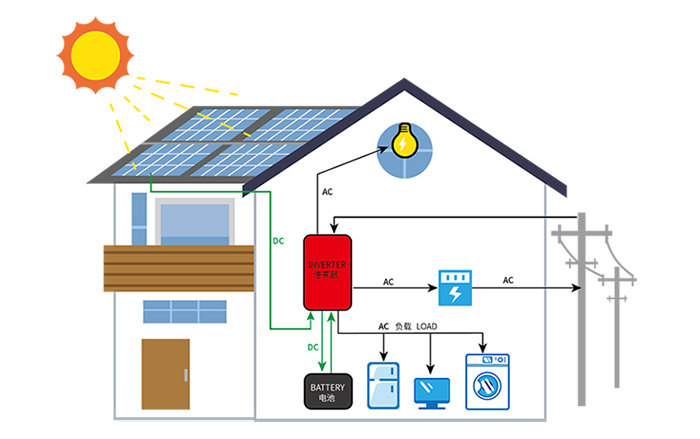
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). Its primary function is to transform DC power sources (such as solar panels, batteries, etc.) into AC power, enabling it to supply electricity to various household appliances, motors, photovoltaic power generation systems, and other equipment. Inverters can convert DC power into AC power at almost any required voltage, current, and frequency while maintaining stable output voltage and frequency to meet diverse application needs.
Inverters are widely used in various fields, including solar power generation, wind power generation, electric vehicles, UPS systems, and household appliances. Among these, solar power generation is one of the main application areas for inverters. In solar power systems, inverters convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity for use in residential and commercial electrical equipment. Additionally, inverters in solar power systems can monitor and control the battery charging and discharging processes to optimize the performance and efficiency of the system.
In the field of electric vehicles, inverters are also critically important. Electric vehicle batteries store DC power, while the motors require AC power to operate. Therefore, inverters convert the DC power from the vehicle’s battery into AC power to supply the motor. At the same time, inverters can regulate the charging and discharging processes of the battery to ensure the vehicle’s performance and longevity.
In summary, inverters are essential electronic devices widely used across various sectors to meet diverse power supply needs. Whether in solar power generation, wind power generation, electric vehicles, UPS systems, or household appliances, inverters play a vital role in providing reliable and efficient power supply.